Using URL Parameters
React-SearchKit can update URL query string parameters with the user selections to enable deep linking.
The URL parameters handling behaves in a similar way as the REST API: when the query state is updated by any component, it is serialized and the URL query string is updated.
When the URL query string changes, React-SearchKit serializes it to the query state triggering automatically an update of all mounted components.
See how the URL query string changes on user input:
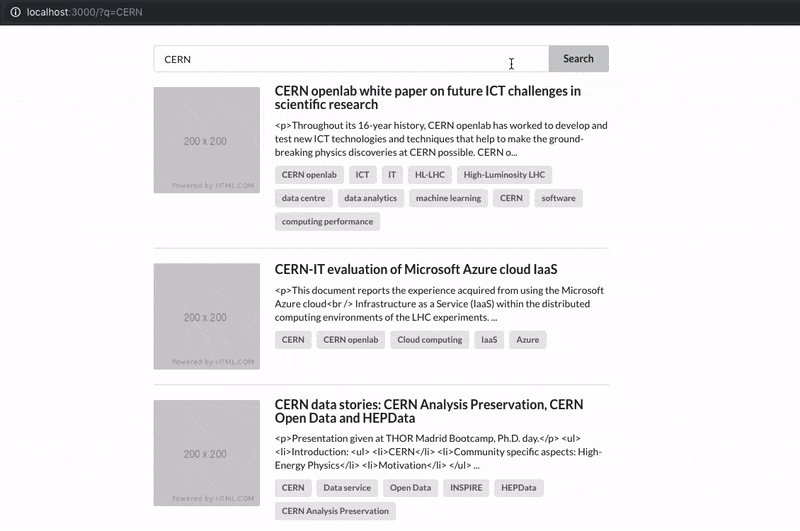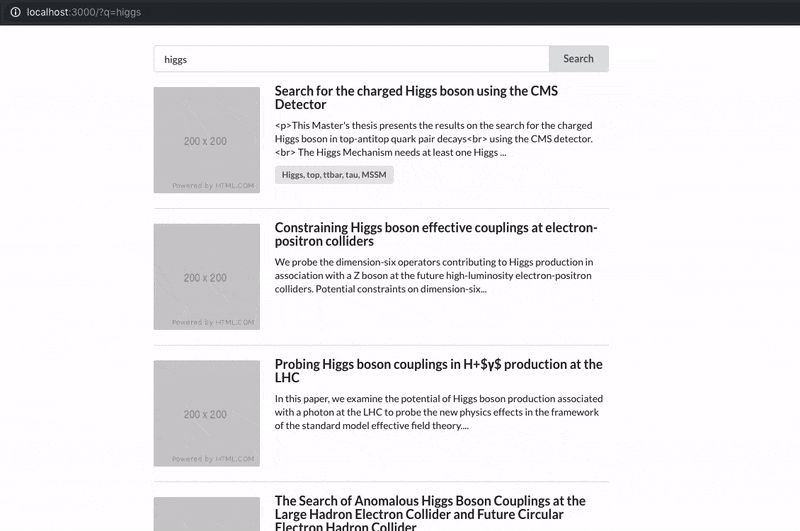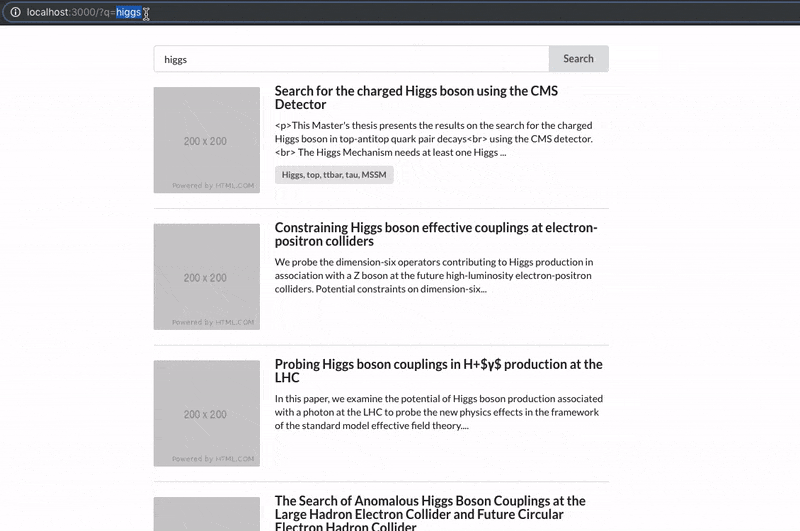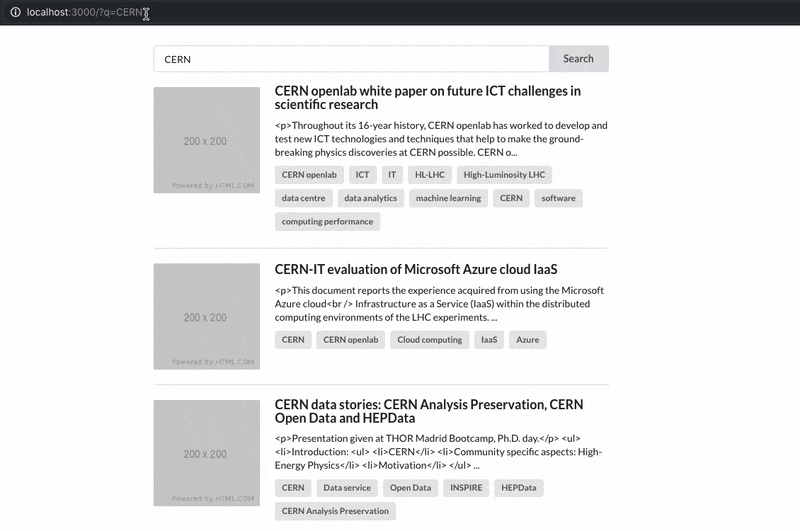
How it works
When loading React-SearchKit, the URL is parsed and each parameter's value is persisted in the query state, defining the initial values.
When the user changes any search criteria using the available components, the query state is updated. The URL is then updated accordingly.
Configure UrlHandlerApi
React-SearchKit uses as default implementation UrlHandlerApi to serialize the query state to the URL query string.
You can configure the way parameters are serialized by injecting custom configuration:
urlParamsMapping: an object to map eachquerystate field to an URL parameterurlParamValidator: a class to validate each parameter's value before updating thequerystateurlParser: an object to parse the URL query string and perform sanitation.keepHistory:trueif each change ofquerystate will push a new state to the browser history.falseif instead URL query string is changed without pushing new states to the browser history.urlFilterSeparator: character(s) separator to be used when serializing filters with children to URL parameters. By default+.
Provide a new mapping
By default, the mapping is the following:
{
queryString: 'q',
sortBy: 'sort',
sortOrder: 'order',
page: 'p',
size: 's',
layout: 'l',
filters: 'f'
}
If you want to change the name of the parameter displayed in the URL, just provide a new mapping to convert the query state, for example:
const myUrlParamsMapping = {
queryString: 'qs',
sortBy: 's',
sortOrder: 'o',
page: 'page',
size: 'size',
layout: 'display',
filters: 'filter'
}
Provide a validator
The parameters validator is called when loading React-SearchKit and parsing the URL to persist parameters values into the query state.
The class must implement a method isValid that returns true if the given param and value is valid, for example:
class MyParamValidator {
isValid = (paramName, paramValue) => {
const valid = ... // your logic
return valid;
};
}
Provide a URL parser
By default, the URL query string is parsed using the library qs. If you want to provide your own parser, then implement an object with a parse method. Given as input the URL query string, it returns an object where each item is the parameter name as key and the parameter value as value.
Note: it is not needed to return all the key/values. If some parameters are not set in the URL, they will be initialised to their default state value.
For example:
class MyUrlParser {
parse = (queryString = '') => {
... // parse the query string
return {
qs: 'CERN',
page: 3
}
}
}
Disable deep linking
Deep linking can be disabled by setting to false the urlHandlerApi.enabled config variable.
Inject the new configuration
You can inject overridden configuration in an object named urlHandlerApi.
const myParamValidator = new MyParamValidator();
const myUrlParser = new MyUrlParser();
<ReactSearchKit
searchApi={...}
urlHandlerApi={{
enabled: true,
overrideConfig: {
keepHistory: false,
urlParamsMapping: {...},
urlParamValidator: myParamValidator,
urlParser: myUrlParser,
}
}}
>
...
</ReactSearchKit>
Implement a new URL handler
If you need to have full control on the way the URL is handled, you can provide your own implementation.
The object needs to implement a get method and a set method:
get: return an object with the same fields as the givenquerystate updating it with the parsed URL parameters values.set: update the URL query string parameters from the givenquerystate.
For example, a new URL handler could be:
class MyUrlParamsHandler {
get = (queryState, pushUpdate) => {
const parsedQS = ...
const newQueryState = {
...queryState,
parseQS['q']
};
return newQueryState;
}
set = stateQuery => {
const urlParams = mapStateToParams(stateQuery);
updateQS(urlParams);
}
}
You can provide the new implementation in the main component.
const myUrlParamsHandler = new MyUrlParamsHandler();
<ReactSearchKit
urlHandlerApi={{
enabled: true
customHandler: myUrlParamsHandler
}}
>
...
</ReactSearchKit>
TL;DR
- You can enabled or disable deep linking with a flag
- You can override specific config providing a
urlHandlerApiconfiguration object as prop - You can implement your own URL handler by implementing the same interface as
UrlHandlerApiand injecting it as propcustomHandler - You can trigger searches by changing URL parameters using the
historylibrary